The COVID-19 coronavirus is spreading across the world. Initially the epicenter was China, with reported cases either in China or in travellers from China. There are now at least four further epicenters: Iran, Italy, Japan and South Korea.
Although the World Health Organisation believes the number of cases in China has peaked and should fall, case reports are climbing from countries previously thought to be resilient due to stronger medical standards and practices.
In a strongly connected and integrated world, the impacts of the disease will go beyond mortality (deaths) and morbidity (people incapacitated or caring for the incapacitated and unable to work).
Companies across the world, irrespective of size, depend on inputs from China – much more so than during the 2002-04 China-centred Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) pandemic.
In 2003 China accounted for less than one twentieth of world trade. It now accounts for one seventh, making it the world’s biggest importer and an integral part of most global production chains.
Just as important to the world economy, panic is distorting spending. Global stock markets have plunged.
Fear is as important as trade
Entire cities in China have closed and travel restrictions have been placed on people entering from infected countries.
The fear of an unknown deadly virus is similar in its psychological effects to the reaction to terrorism threats and produces a high level of stress, often with longer-term consequences.
A large number of people feel at-risk at the onset of a pandemic, even if their actual risk of dying is low.
The International Monetary Fund expects COVID-19 to knock 0.4 points off China’s economic growth target of 5.6% and 0.1 points off global growth, an assessment it will continue to update.
On Monday the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development sliced 0.8 points off its forecast for China’s growth and 0.5 points off its forecast for Australian growth.
As part of a large research project in the Centre for Excellence in Population Ageing Research (CEPAR) at the Australian National University, we have applied experience gained from evaluating the impact of SARS for the World Health Organisation in 2003 and 2006 to seven scenarios for COVID-19:
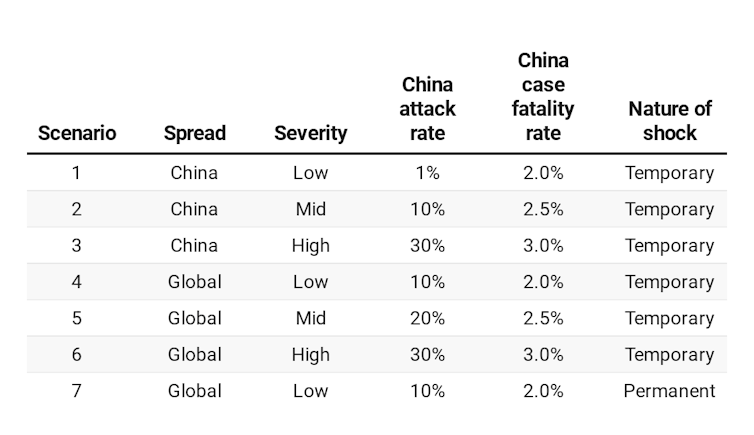
The scenarios vary the attack rate (the proportion of the total population contracting the virus), the mortality rate (the proportion of total population who dies), whether epidemic is a one-off (essentially temporary) or recurrs each year (essentially permanent), and whether it spreads globally or is largely confined to China.
Australian faces a significant hit to GDP
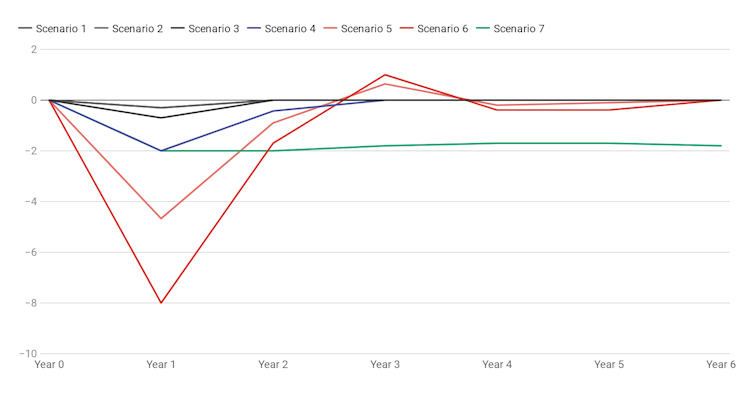
We find that in the four scenarios where the epidemic goes global, Australia’s GDP which in the 12 months to December grew just 1.7%, would suffer a hit in the first year of between 2% and 7.9%, most likely sending GDP backwards (a recession).
In all countries the sharp hit to growth would be followed by a gradual recovery.
The results are very sensitive to the assumptions used, including government responses in each country.
In the short term, central banks and treasuries will need to make sure disrupted economies continue to function.
Australia: percentage change in real GDP
While cutting interest rates is an option, the shock will require a mix of monetary, fiscal and health policy responses. Quarantining affected people and reducing large scale social interaction would be an effective response.
Wide dissemination of good hygiene practices can be a low cost and highly effective response that can also reduce the extent of contagion and keep down the social and economic cost.
The longer-term responses are even more important.
Many governments have been reluctant to invest sufficiently in their health care systems, especially in public systems in less developed countries where many infectious diseases are likely to originate.
Investments in overseas public health matter
The idea that any country can be an island in an integrated global economy is being proved wrong.
Poverty kills people. However, the outbreak of COVID-19 shows that diseases, potentially generated in poor countries due to overcrowding, poor public health and interaction with wild animals, can kill people of any socioeconomic group in any country.
There needs to be vastly more investment in public health and development in the richest but also, and especially, in the poorest countries.
Read more: High-tech shortages loom as coronavirus shutdowns hit manufacturers
Our study suggests big economic costs in countries such as Australia can be avoided through global cooperative investment in public health in all countries.
We have known this for decades, yet politicians continue to ignore the scientific and economic evidence about the role of global public health in improving the quality of life and driving economic growth for us all.
By Warwick McKibbin, Chair in Public Policy, ANU Centre for Applied Macroeconomic Analysis (CAMA), Crawford School of Public Policy, Australian National University and Roshen Fernando, PhD Student in Economic Policy, Australian National University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.












