Tambri Housen, Australian National University; Amy Elizabeth Parry, Australian National University, and Meru Sheel, Australian National UniversityOne thing many of us want to know is for how long people who have SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, are able to pass it on to someone else.
Let’s look at what the science tells us so far.
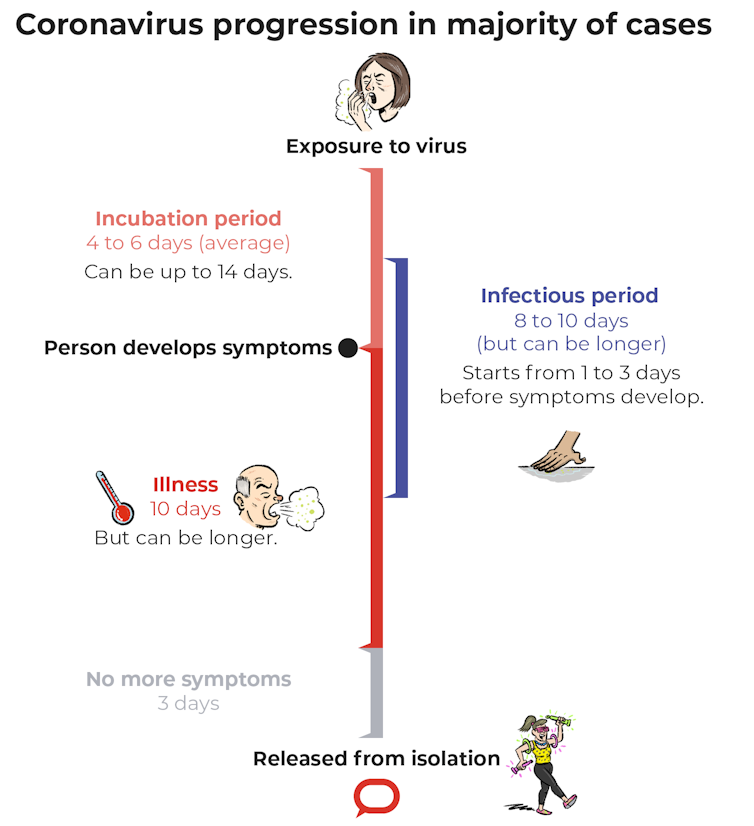
How long does it take to get sick?
The “incubation period” is the time between being exposed to the virus and the onset of symptoms.
For COVID-19, the incubation period ranges from 1 to 14 days. But most people who develop COVID-19 symptoms do so 4 to 6 days after exposure.
How long are you infectious?
The “infectious period” means the time you’re able to spread the virus to someone else.
For COVID-19, there is emerging evidence to suggest the infectious period may start 1 to 3 days before you develop symptoms.
The most infectious period is thought to be 1 to 3 days before symptoms start, and in the first 7 days after symptoms begin. But some people may remain infectious for longer.
Commonly reported symptoms for COVID-19 – such as fever, cough and fatigue – usually last around 9 to 10 days but this can be longer.
Why are some people infectious for longer?
Typically with viruses, the higher the viral load (the more virus circulating in the body), the higher the risk of transmission through known transmission pathways.
A study conducted in Hong Kong looking at viral load in 23 patients diagnosed with COVID-19 found higher viral loads in the first week of illness.
Another study from China looking at 76 hospitalised patients found that by 10 days after symptom onset, mild cases had cleared the virus. That is, no virus was detectable through testing.
However, severe cases have much higher viral loads and many continue to test positive beyond the 10 days after symptoms start.
So the more severe the illness and the higher the viral load, the longer you continue to shed the virus and are infectious.
When are you no longer infectious?
If someone has been symptom-free for 3 days and they developed their first symptoms more than 10 days prior, they are no longer considered to be infectious.
But we’re not sure whether people are infectious when they have recovered but the virus can still be detected in their bodies.
One study from Hong Kong found the virus could be detected for 20 days or longer after the initial onset of symptoms in one-third of patients tested.
Another study from China found found the virus in a patients’ faecal samples five weeks after the first onset of symptoms.
But the detection of the virus doesn’t necessarily mean the person is infectious. We need more studies with larger sample sizes to get to the bottom of this question.
Should you get tested again before going back into the community?
Due to a global shortage of coronavirus tests, the Commonwealth and state governments have strict criteria about who should be tested for COVID-19 and when.
People who have been self-quarantining, because they had contact with a confirmed case of COVID-19 and have completed their 14-day quarantine period without developing symptoms, can return to the community. There is no requirement to be tested prior to returning to the community. It is, however, recommended they continue to practise social distancing and good hygiene as a precaution.
The requirements are different for people who have been diagnosed with COVID-19.
At present, re-testing people who have experienced mild illness, and have recovered from COVID-19 is not recommended. A person is considered safe to return to the community and discontinue self-isolation if they are no longer infectious. This means they developed their first symptoms more than 10 days prior and have not experienced any symptoms for at least 3 days (72 hours).
For people who have been hospitalised with more severe illness, the testing requirements before discharge are different. They will have two swabs taken 24 hours apart to check if they have cleared the virus. If the swabs are both negative, they can be discharged and don’t require further self-isolation.
If one or both tests are positive but the person is well enough to go home, they must continue to self-isolate for at least 10 days since they were discharged from hospital and they have not experienced any symptoms for at least 3 days.
There are also different testing requirements for people working or living in high-risk settings. If you work or live in a high-risk setting you should consult with your health care provider on re-testing requirements.
Tambri Housen, Epidemiologist | Senior Research Fellow, National Centre for Epidemiology and Population Health, Australian National University; Amy Elizabeth Parry, Epidemiologist | PhD Candidate, National Centre for Epidemiology and Population Health, Australian National University, and Meru Sheel, Epidemiologist | Senior Research Fellow, Australian National University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.












