Andrew Christ, University of Vermont and Paul Bierman, University of Vermont
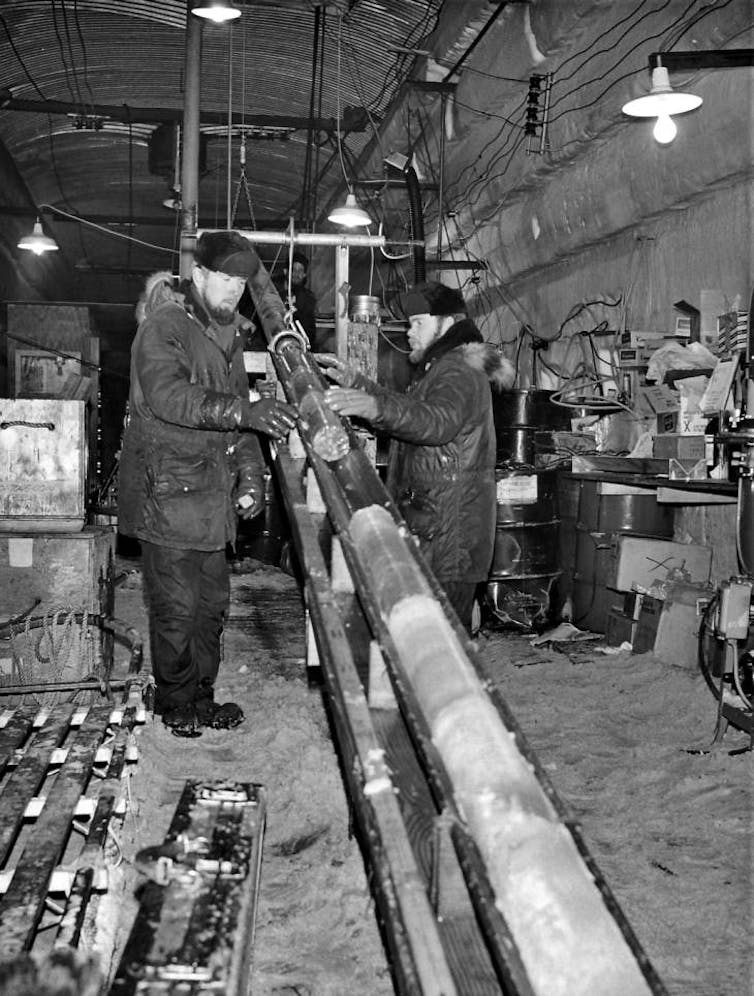
In 1963, inside a covert U.S. military base in northern Greenland, a team of scientists began drilling down through the Greenland ice sheet. Piece by piece, they extracted an ice core 4 inches across and nearly a mile long. At the very end, they pulled up something else – 12 feet of frozen soil.
The ice told a story of Earth’s climate history. The frozen soil was examined, set aside and then forgotten.
Half a century later, scientists rediscovered that soil in a Danish freezer. It is now revealing its secrets.
Using lab techniques unimaginable in the 1960s when the core was drilled, we and an international team of fellow scientists were able to show that Greenland’s massive ice sheet had melted to the ground there within the past million years. Radiocarbon dating shows that it would have happened more than 50,000 years ago. It most likely happened during times when the climate was warm and sea level was high, possibly 400,000 years ago.
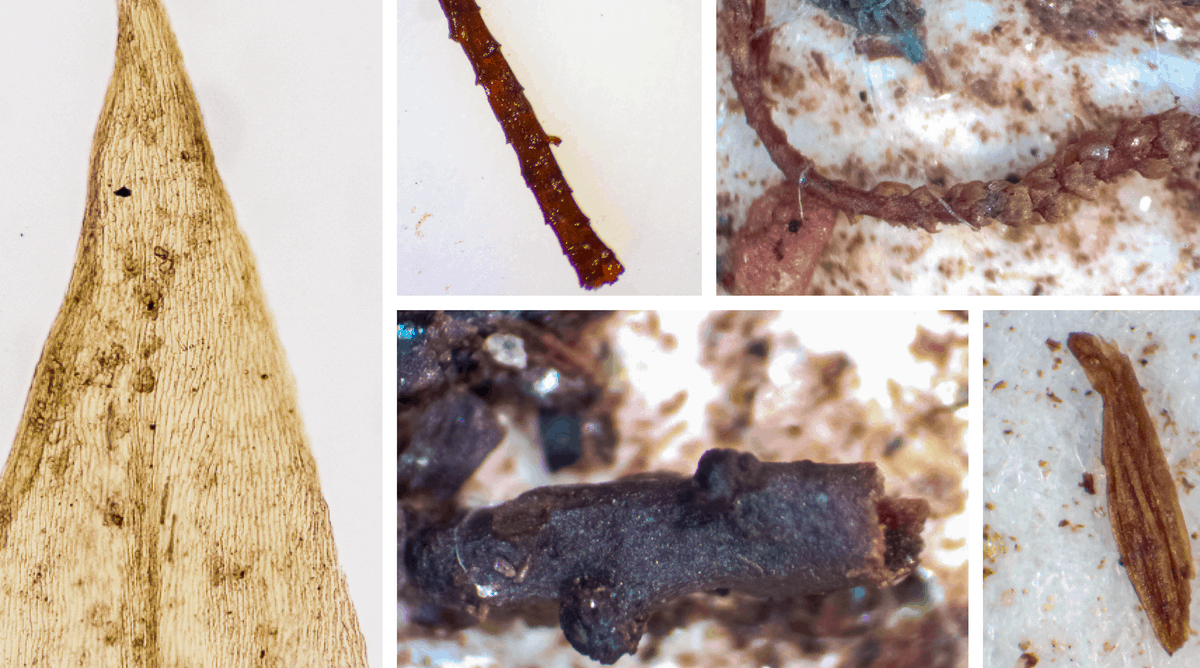
And there was more. As we explored the soil under a microscope, we were stunned to discover the remnants of a tundra ecosystem – twigs, leaves and moss. We were looking at northern Greenland as it existed the last time the region was ice-free. Our peer-reviewed study was published on March 15 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.

https://www.youtube.com/embed/Ota2-eEN41w?wmode=transparent&start=0 Paul Bierman, a geomorphologist and geochemist, describes what he and his colleagues found in the soil.
With no ice sheet, sunlight would have warmed the soil enough for tundra vegetation to cover the landscape. The oceans around the globe would have been more than 10 feet higher, and maybe even 20 feet. The land on which Boston, London and Shanghai sit today would have been under the ocean waves.
All of this happened before humans began warming the Earth’s climate. The atmosphere at that time contained far less carbon dioxide than it does today, and it wasn’t rising as quickly. The ice core and the soil below are something of a Rosetta Stone for understanding how durable the Greenland ice sheet has been during past warm periods – and how quickly it might melt again as the climate heats up.
Secret military bases and Danish freezers
The story of the ice core begins during the Cold War with a military mission dubbed Project Iceworm. Starting around 1959, the U.S. Army hauled hundreds of soldiers, heavy equipment and even a nuclear reactor across the ice sheet in northwest Greenland and dug a base of tunnels inside the ice. They called it Camp Century.
It was part of a secret plan to hide nuclear weapons from the Soviets. The public knew it as an Arctic research laboratory. Walter Cronkite even paid a visit and filed a report.
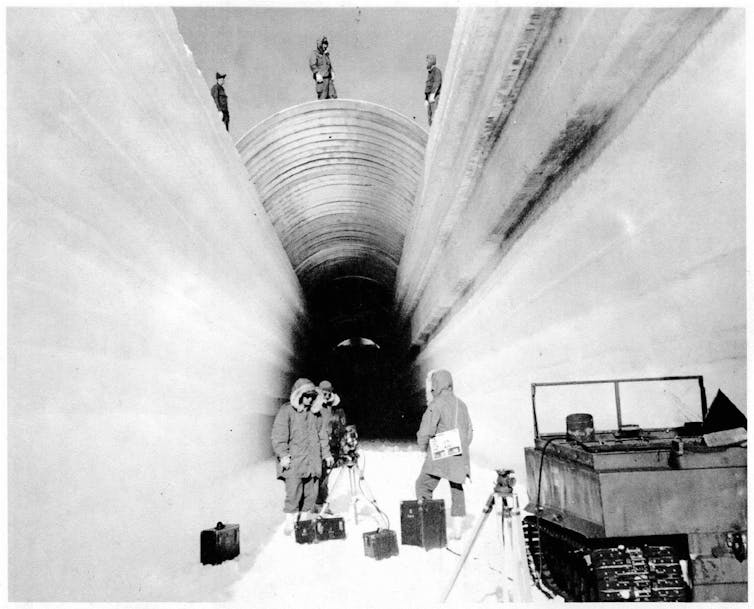

Camp Century didn’t last long. The snow and ice began slowly crushing the buildings inside the tunnels below, forcing the military to abandon it in 1966. During its short life, however, scientists were able to extract the ice core and begin analyzing Greenland’s climate history. As ice builds up year by year, it captures layers of volcanic ash and changes in precipitation over time, and it traps air bubbles that reveal the past composition of the atmosphere.
One of the original scientists, glaciologist Chester Langway, kept the core and soil samples frozen at the University at Buffalo for years, then he shipped them to a Danish archive in the 1990s, where the soil was soon forgotten.
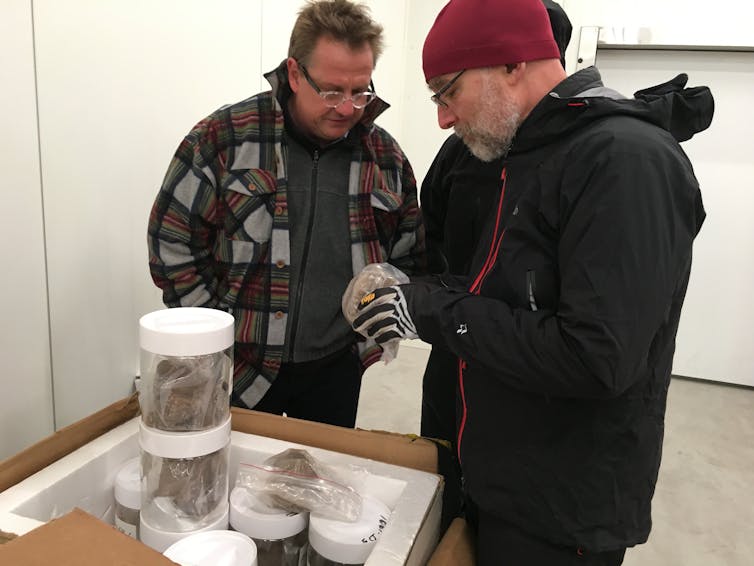
A few years ago, our Danish colleagues found the soil samples in a box of glass cookie jars with faded labels: “Camp Century Sub-Ice.”

A surprise under the microscope
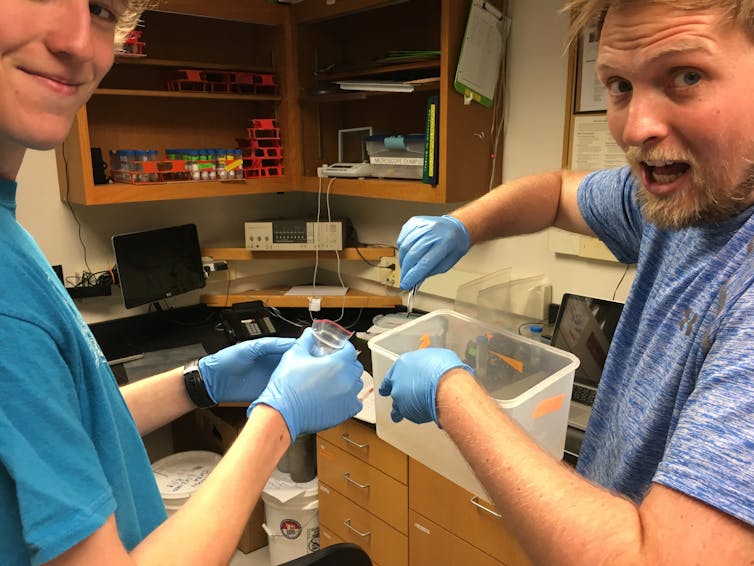
On a hot July day in 2019, two samples of soil arrived at our lab at the University of Vermont frozen solid. We began the painstaking process of splitting the precious few ounces of frozen mud and sand for different analyses.
First, we photographed the layering in the soil before it was lost forever. Then we chiseled off small bits to examine under the microscope. We melted the rest and saved the ancient water.
Then came the biggest surprise. While we were washing the soil, we spotted something floating in the rinse water. Paul grabbed a pipette and some filter paper, Drew grabbed tweezers and turned on the microscope. We were absolutely stunned as we looked down the eyepiece.
Staring back at us were leaves, twigs and mosses. This wasn’t just soil. This was an ancient ecosystem perfectly preserved in Greenland’s natural deep freeze.

Dating million-year-old moss
How old were these plants?
Over the last million years, Earth’s climate was punctuated by relatively short warm periods, typically lasting about 10,000 years, called interglacials, when there was less ice at the poles and sea level was higher. The Greenland ice sheet survived through all of human history during the Holocene, the present interglacial period of the last 12,000 years, and most of the interglacials in the last million years.
But our research shows that at least one of these interglacial periods was warm enough for a long enough period of time to melt large portions of the Greenland ice sheet, allowing a tundra ecosystem to emerge in northwestern Greenland.
We used two techniques to determine the age of the soil and the plants. First, we used clean room chemistry and a particle accelerator to count atoms that form in rocks and sediment when exposed to natural radiation that bombards Earth. Then, a colleague used an ultra-sensitive method for measuring light emitted from grains of sand to determine the last time they were exposed to sunlight.
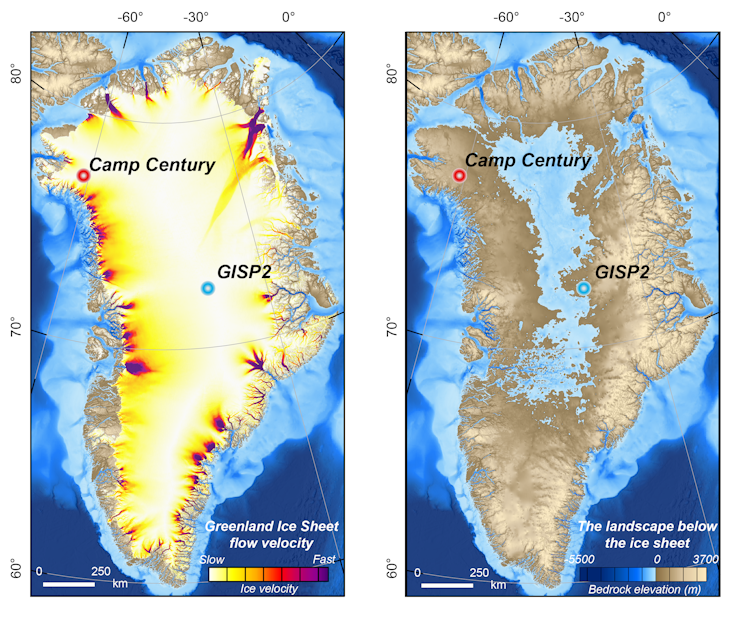
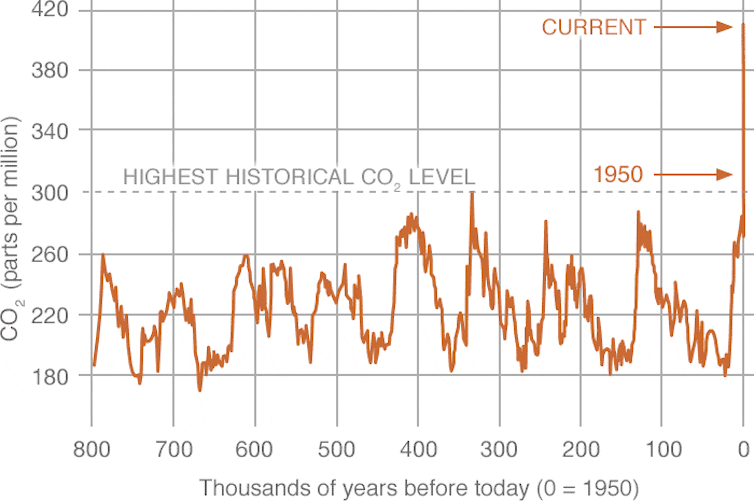
The million-year time frame is important. Previous work on another ice core, GISP2, extracted from central Greenland in the 1990s, showed that the ice had also been absent there within the last million years, perhaps about 400,000 years ago.
Lessons for a world facing rapid climate change
Losing the Greenland ice sheet would be catastrophic to humanity today. The melted ice would raise sea level by more than 20 feet. That would redraw coastlines worldwide.
About 40% of the global population lives within 60 miles of a coast, and 600 million people live within 30 feet of sea level. If warming continues, ice melt from Greenland and Antarctica will pour more water into the oceans. Communities will be forced to relocate, climate refugees will become more common, and costly infrastructure will be abandoned. Already, sea level rise has amplified flooding from coastal storms, causing hundreds of billions of dollars of damage every year.
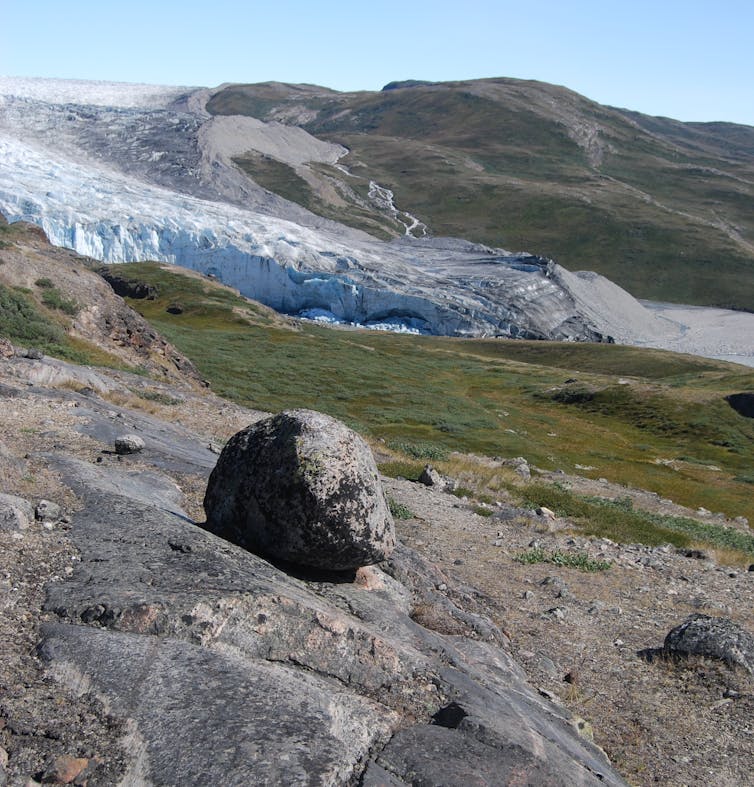

The story of Camp Century spans two critical moments in modern history. An Arctic military base built in response to the existential threat of nuclear war inadvertently led us to discover another threat from ice cores – the threat of sea level rise from human-caused climate change. Now, its legacy is helping scientists understand how the Earth responds to a changing climate.
This article was updated to correct the chart caption to 417 ppm.
Andrew Christ, Postdoctoral Fellow and Lecturer in Geology, University of Vermont and Paul Bierman, Fellow of the Gund Institute for Environment, Professor of Geology and Natural Resources, University of Vermont
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.












