Peter Martin, Crawford School of Public Policy, Australian National University
It would be a waste if the Friday’s mammoth Retirement Incomes Review was remembered only for its finding that increases in employers compulsory superannuation contributions come at the expense of wages.

That has long been assumed, and is what was intended when compulsory super was set up.
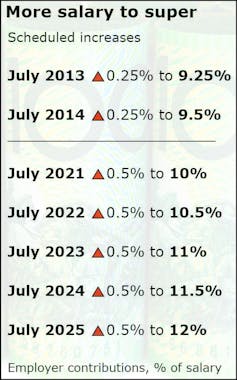
Compulsory super contributions are set to increase in five annual steps of 0.5% of salary between 2021 and 2025.
These are much bigger increases than the earlier two of 0.25% in 2012 and 2013.
And the wage rises they will be taken from will be much lower. The latest figures released on Wednesday point to shockingly low annual wage growth of 1.4%.
Should each of the scheduled increases in employers compulsory super knock 0.4 points off wage growth (which is what the review expects) annual wage growth would sink from 1.4% to 1%.
Private sector wage would sink from 1.2% to 0.8%, in the absence of something to push it back up.
Because inflation will almost certainly be higher than 1%, it means the buying power of wages would go backwards, all for the sake of a better life in retirement.
The review presents the finding starkly. Lifting compulsory super contributions from 9.5% of salary to 12% will cut working-life incomes by about 2%.
And for what? It’s a question the review spends a lot of time examining.
Most retirees have enough
The review dispenses with the argument that the goal of a retirement income system should be “aspirational”, or to provide people with higher income in retirement than they had in their working lives.
It finds that for retirees presently aged 65-74 the replacement rates for middle to higher income earners are generally adequate.
Many lower-income earners get more per year in retirement than they got while working.
If the increases in compulsory super proceed as planned, this will extend to the bottom 60% of the income distribution.
They’ll enjoy a higher standard of living in retirement than while working (and will enjoy a lower standard of living while working than they would have).
Most retirees die with most of what they had when they retired, leaving it as a bequest. They are reluctant to “eat into” their super and other savings because of concerns about possible future health and aged care costs, and concerns about outliving savings.
The review quite reasonably sees this as a betrayal of the purpose of government-supported super, saying
superannuation savings are supported by tax concessions for the purpose of retirement income and not purely for wealth accumulation
It’s the pension that matters
The pension does what super cannot. It provides a buffer for retirees whose income and savings fall due to market volatility, and for those who outlive their savings. 71% of people of age pension age get it or a similar payment. More than 60% of them get the full pension.
If there’s one key message of the review, it is this: it is the pension rather than super that matters for maintaining living standards in retirement, which is what the review was asked to consider.
It is also cost-effective compared to the growing budgetary cost of the super tax concessions.
The age pension costs 2.5% of GDP and is set to fall to 2.3% of GDP over the next 40 years as the super system matures and tighter means tests bite.
Treasury modelling prepared for the review shows that if more money is directed into super and away from wages as scheduled, the annual budgetary cost of the super tax concessions (mostly directed will exceed the cost of the pension by 2050.
There’s a real retirement income problem
A substantial proportion of Australians, about 30%, are financially worse off in retirement than while working, and they are people neither super nor the pension can help.
Mostly they are older Australians who have lost their jobs and cannot get new ones before they before eligible for the age pension or become old enough to get access to their super. Often they’ve left the workforce due to ill health or to care for others and are forced to rely on JobSeeker, which is well below the poverty line.
It’s much worse if they rent privately. About one quarter of retirees who rent privately are in financial stress, so much so that the review finds even a 40% increase in the maximum Commonwealth Rent Assistance payment wouldn’t be enough to get them a decent standard of living in retirement.
No recommendations, but findings aplenty
The review was not asked to produce recommendations. Instead, while noting that much of the system works well, it has pointed to things that need urgent attention.
It finds that pouring a greater proportion of each pay packet into the hands of super funds is not one of them, and in the present unusual circumstances could cost jobs as employers who can’t take the extra cost out of wages take it out of headcount.
The government will make a decision about whether to proceed with the legislated increase in compulsory super in its May budget, just before the first of the five increases due in July.
Peter Martin, Visiting Fellow, Crawford School of Public Policy, Australian National University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.












