David Blunck, Oregon State University
As firefighters tried to protect homes near Lake Tahoe from one of California’s largest fires on record, they battled, windblown embers that kept sparking new small fires, some well away from the fire line.
Those embers, also known as firebrands, were a powerful and dangerous reminder that protecting homes is about more than avoiding a wall of flames.
Firebrands are pieces of flaming material that break off from burning vegetation or structures and are transported through the air. They particularly become a problem when heat and drought dry out grasses and trees and the wind picks up. Homes and other structures are at higher risk when they have dry fuel, such as leaves, needles or wood chips, on the structure or nearby.
That risk, and how it can easily be overlooked, crystallized for me in September 2020 when my parents were put on notice to prepare to evacuate as a fire neared their home in Oregon. I have studied wildfires for years, particularly how they spread through firebrands. Yet this threat made it real.
What protecting a home looks like
I was not concerned about a wall of flames reaching my parents’ home – they had a lush and green yard that was unlikely to ignite. Instead, what concerned me was whether my parents were prepared for ignition by firebrands.
Firebrands can travel over a mile by the wind and can be a major cause of spreading fires. In the Tahoe region, for example, firefighters couldn’t just focus on the main fire line in summer 2021 – they also had to patrol for spot fires.
At my parents’ home and several of their neighbors’, I used a leaf blower to clear potential ignition sources. I removed dried leaves in gutters and needles in valleys of roofs, and watered the dry mulch near houses.
I asked myself, if a lighted match or matches were dropped at a location, could they start a fire? If so, the potential fuel needed to be removed. In every home that I visited, I found locations where firebrands could potentially ignite flammable materials, despite the homeowners’ best preparations.
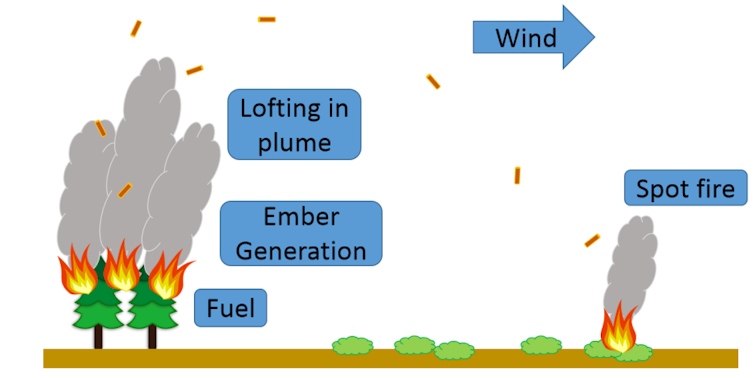
What surprised me at the time was how little time people applied to preparing for firebrands, despite going to great lengths to protect their homes by watering the grounds. What I realized was that my parents and their neighbors, like many of us, envisioned protecting homes as stopping a wall of flames from reaching their homes. They did not appreciate that in some cases the greater threat could blow in by the wind.
Three steps to firebrand-started fires
Fire scientists talk about spot fires as occurring in three steps: how firebrands are generated, how they are carried by the wind and how they land and ignite fuel. Fire scientists, including those from my research group, are actively studying each of these steps to be able to better predict and ultimately reduce the risks to communities from firebrands.
Firebrands are generated from burning vegetation or structures. Sizes of the firebrands can vary, but can be as small as several millimeters square.
Firebrands can come from burning pieces of bark, branches, cones or needles if the source is wildfires. For urban fires, firebrands can come from roofing, siding, particle boards or other flammable materials.
Over the past two decades, efforts studying generation of firebrands have often focused on quantifying the number of firebrands that land at particular locations as trees or other vegetation burns. More recently, researchers are working to estimate the total number of firebrands that are released when objects burn.
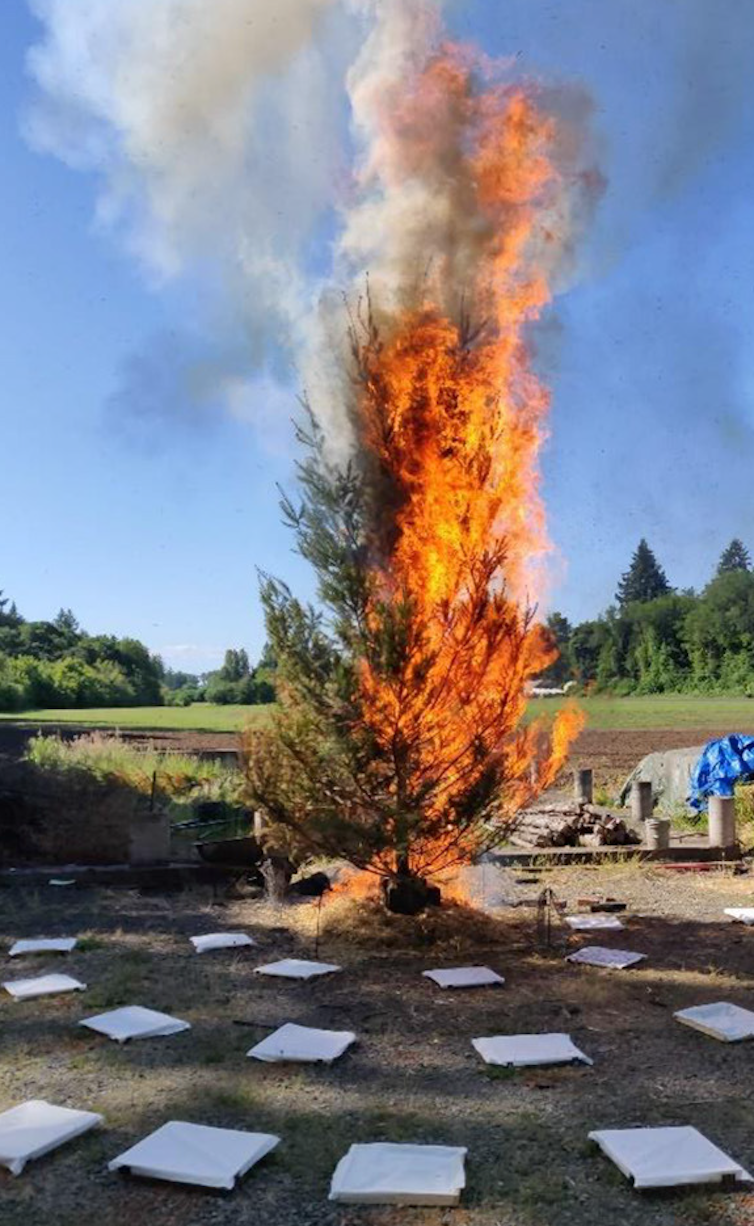

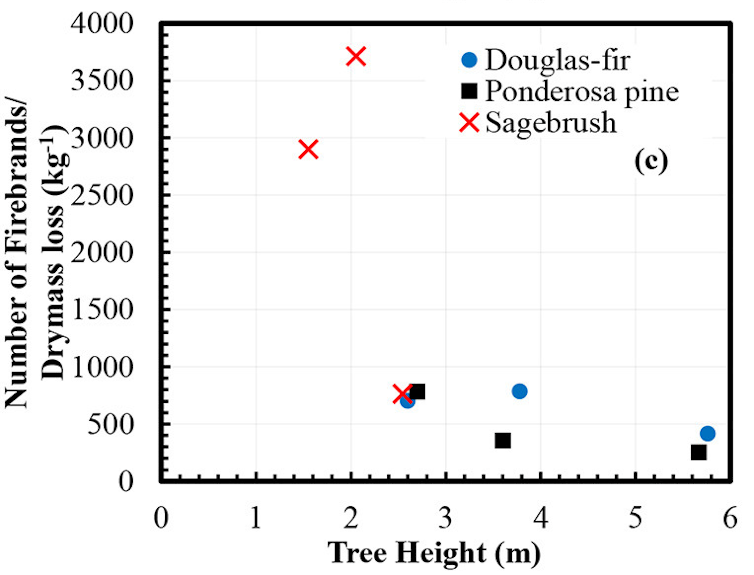
To estimate how many firebrands a fire generates, we set fire-resistant fabric squares around burning trees and shrubs, such as Douglas fir and sagebrush, and collected the firebrands that landed. By determining the total number of firebrands per unit of mass of the tree or shrub that burns, we can incorporate data into computer models to estimate the total number of firebrands released in a fire and where they spread. Ultimately, we hope these models can be used to better understand risks associated with wild or urban fires.
Many research efforts have focused on developing models that capture the physics of how firebrands are transported or where firebrands are most likely to land. The nature of the burning of firebrands as they are being transported is an important factor. Firebrands can be flaming or smoldering. Both can cause new fires.
The third step is ignition of fuels – like fencing, mulch and needles – after firebrands land. Researchers are investigating the heating potential or temperature of firebrands. Understanding this information is critical for implementing building codes and standards and best practices to better protect homes. We’re also working to better understand which characteristics of the fuels determine whether they ignite.
How can homeowners reduce the risk?
So what can homeowners do to protect themselves from the risk of spot fires?
First, start with shifting your mindset about preparation to not if, but when a fire will occur nearby. I will admit that, as a homeowner who lives near a forest, I allow pine needles and leaves to accumulate on my roof. I make the excuse that I will have time to prepare in an actual fire. Yet, as I consider preparing for “when a fire” will be near me, rather than “if,” I feel more of a sense of urgency and responsibility.
Second, people in fire-prone areas need to educate themselves about potential ignition sources. Note that locations that are fire-prone are expanding. My parents’ home hadn’t been threatened by fires in the 30 years they had lived there – until 2020. One resource when figuring out how to audit a home’s risk is the National Fire Protection Association.
Certainly, at a minimum people to need to remove flammable material from on or near homes. In addition, they should consider ignition sources from structures such as decks and ensure that firebrands cannot be pulled into homes through ventilation ducts or other methods. Putting screens on windows and over ventilation ducts, using 1/8-inch holes, can be a simple, low-cost and highly effective way to stop firebrands from entering a house.
Third, consistently act to monitor and eliminate ignition sources, such as needles or leaves, that can gradually accumulate with time. Often it takes little effort to remove the debris, but it requires constant monitoring and prioritizing removal.
[Over 100,000 readers rely on The Conversation’s newsletter to understand the world. Sign up today.]
Certainly taking steps to educate, audit and then remove ignition sources from firebrands will not stop all fires from spreading to homes. But these steps will save many homes and help to reduce the risk to fire responders and communities.
David Blunck, Associate Professor School of Mechanical, Industrial, and Manufacturing Engineering, Oregon State University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.












