Caitjan Gainty, King’s College London and Agnes Arnold-Forster, University of Bristol
Smallpox killed countless millions – 300 million people in the 20th century alone – before it was finally declared eradicated on May 8 1980. It was a momentous day, marking what the current director general of the World Health Organization, Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, called the greatest “public health triumph in world history”.
Smallpox, as one researcher has emphasised, “was eradicated solely through vaccination”. Today, this achievement feels particularly encouraging and seems ready for a reboot as governments worldwide tell the public that the COVID vaccine will soon end the pandemic and return life to normal.
Worldwide, advance reviews are flooding in. Vaccines are a “light at the end of the tunnel”, our ticket to “normality”. They have brought a “real end” into sight. From New York governor Andrew Cuomo came the inevitable military analogy: the vaccine was no less than “the weapon that is going to win the war”.
The current vaccination campaigns are not attempting to eradicate SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID. But, based on the history of smallpox vaccination, even the much lower bar of herd immunity will be difficult to clear if we pin so much of our hope on vaccination.
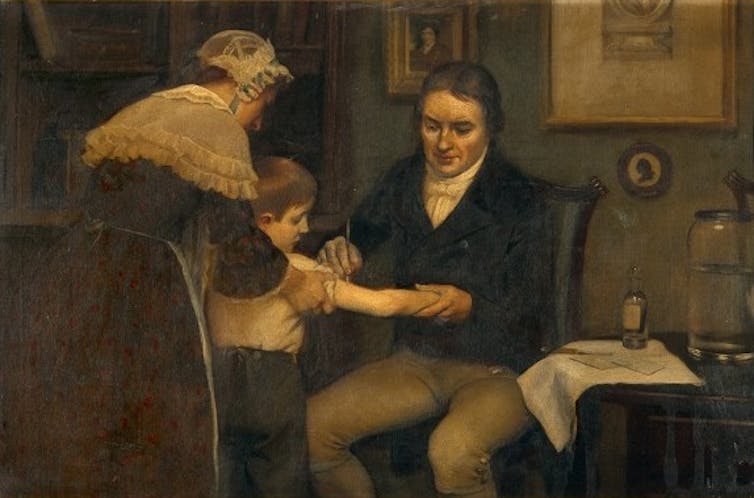
Although the eradication of smallpox is often held up as proof of the definitive success of vaccines, it should not be forgotten that smallpox raged for centuries before it was finally brought to an end. One of the first steps towards eradication took place in 1796 when, as the somewhat apocryphal story goes, Edward Jenner injected pus extracted from a dairymaid’s cowpox lesion into the arm of his gardener’s eight-year-old son.

The following 150 years were marked by concern about the vaccine’s efficacy, safety and side-effects. As late as 1963, British doctors were still alarmed by the slow uptake of routine smallpox vaccination, warning that this “indifference” would require a “vast programme of re-education”.
Hesitancy was not the only problem. Well into the 20th century, vaccines were unequally distributed around the globe, and periodic outbreaks ensured that smallpox remained endemic in much of the world, particularly in developing countries.
By 1967, when the WHO launched the ten-year intensified smallpox eradication programme, four other eradication efforts (hookworm, yellow fever, yaws and malaria) had already failed, and many involved in such programmes had become sceptical about eradication as a goal at all. Indeed, the 1966 director general of the WHO, Marcelino Candau, believed that disease eradication was simply not possible.
What they had come to realise was that vaccines alone are not enough to contain or eradicate a disease. Instead, it would be essential to combine technological developments – such as the introduction of heat-stable freeze-dried vaccines and the bifurcated (two-pronged) needle – with efforts such as surveillance, case finding, contact tracing, ring vaccination (controlling an outbreak by vaccinating a ring of people around each infected individual), and communication campaigns to find, track and inform affected people.
This sort of programme would encounter various challenges from funding to political strife to cultural practices and norms. It would also cost a whopping 20% of the WHO’s budget and take a decade of intensive labour – and come at the expense of other, more basic healthcare interventions. But eventually it succeeded. Smallpox, outside of the lab at least, was gone.
All this time and coordinated effort, even though smallpox was in some ways an ideal candidate for eradication. For one thing, its symptoms were so obvious that it was easy to identify and track, and so also easier to contain. And smallpox was a disease unique to humans, affecting no other animals. Its eradication from human populations was its eradication from the planet.
Low-tech public health strategies
The history of smallpox eradication makes it apparent that high-tech vaccinations only work when they are effectively combined with low-tech public health strategies. These low-tech strategies include isolation and quarantine, and especially tracking and tracing, as well as the increasingly elusive elements of public trust and effective communication.
Perhaps most clearly, the smallpox story shows that the control of COVID requires a global effort that attends to local needs. This is partly an ethical imperative, partly a practical one. We live in a world with remarkably porous borders, even in times of lockdown. If the smallpox eradication programme has taught us anything, it’s that lasting reprieve from pandemic disease is difficult, if not impossible, to achieve if nations insist on acting in seclusion.
The glorification of the COVID vaccines follows a well-worn track in its presumption that the arrival of a vaccine heralds the pandemic’s end. Yet in the case of smallpox, our most successful vaccine story to date, this has required the glossing over of centuries of suffering and death and the intense public health struggle to contain the disease. Vaccination did not end smallpox. That was done by a small army of people and organisations working intensively and cooperatively across the globe, inventing and improvising a series of public health measures.
We have inherited a recent medical and political past that values quick fixes and cures, blindly embracing these to the exclusion of the messy details of how healthcare actually works. It is not just the final eradication of smallpox, then, but also the personal and public health havoc it wreaked across the centuries that should guide our efforts. For these supply the context we need to create reasonable expectations about what the end of our current pandemic might look like and what it will take to get there.
Caitjan Gainty, Lecturer in the History of Science, Technology and Medicine, King’s College London and Agnes Arnold-Forster, Research Fellow, History of Medicine and Healthcare, University of Bristol
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.












