Dinusha Mendis, Bournemouth University
NFTs or non-fungible tokens first captured the public imagination when a digital collage by an artist named Beeple sold for US$69 million (£51 million) at Christie’s in March 2021. Since then, there has been an explosion in the use of these units for storing digital content, which are bought and sold using online ledgers known as blockchains.
Since that initial connection with art, we are seeing NFTs being used in numerous other ways. Notably, many are being traded as collectables on exchanges like OpenSea and Rarible. Lately, for example, a series of 8,888 adorable “Pudgy Penguins” made a splash, each reflecting its own unique characteristic, with one selling for a record 150 ethereum (about US$500,000).
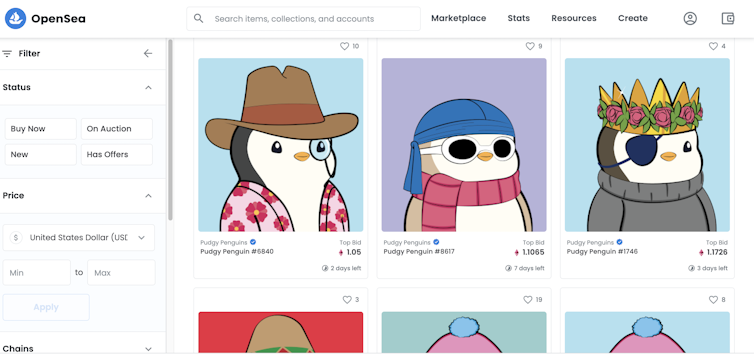
Yet whether it is a remarkable piece of digital artwork or a cute digital penguin, NFTs are essentially tradeable jpegs or gifs. Unlike physical collectables, an NFT owner will not be able to display the asset in their home – except on a screen. They might think they could display it on a website, but this isn’t necessarily the case. So what is someone actually getting when they buy an NFT, and what do they truly own from a legal perspective?
The new frontier
To understand NFTs, it is important to understand what is meant by “fungible”. Fungible is derived from the Latin verb fungi, meaning to perform. In the broader context, this means interchangeable and relates to whether something can be exchanged.
Money is fungible, in the sense that you can buy a commodity worth £10 with any £10 note; it doesn’t matter which one you use. On the other hand, NFTs cannot be exchanged like for like with another. They are each one of a kind, or one of a limited edition.
Content sold as NFTs can be created in many ways. It can be computer-generated, which was the basis for the production of 10,000 unique CryptoPunks in 2017.
It can reflect a collaborative work, such as the English singer-songwriter Imogen Heap’s series of music NFTs, “Firsts”. These involved her improvising alongside visuals provided by artist Andy Carne. Or NFTs can represent a single work, such as Beeple’s artwork; or a series of items, such as the Kings of Leon’s “NFT Yourself” series in which the assets on offer included music albums with unique features and special concert tickets.
Limited rights
NFTs allow the owner of a limited work or collection to reach their audience directly. Whereas previously it was not possible to sell something like the first ever tweet, or a taco-themed gif, or indeed a piece of art online, now individuals, companies or cultural organisations can do so as long as they are the rightful owner.
The creator can do this because, according to UK copyright law, copyright arises automatically when a work is created – as long as it reflects the “author’s own intellectual creation”. This means that the creator of a work is the owner of the copyright, and can do what they want with it.
When someone buys an NFT from the creator, they obtain ownership in the sense that it becomes their property. After all, an NFT is a digital certificate of ownership representing the purchase of a digital asset, traceable on the blockchain.
But the NFT holder does not have any other rights to the work. This includes those offered under copyright law, such as the right of communication to the public (in other words, making the asset available to the world at large), or the rights of adaptation or reproduction.
The situation is the same if you buy a physical collectable. Owning a painting does not automatically give you the right to display it in public. It also doesn’t give you the right to sue for infringement of copyright if someone reproduces the image in the painting without permission. To obtain such rights, you either need to be the copyright owner of the work or have the copyright assigned to you by the creator (in writing and signed).
The trouble with online content is that, by virtue of its digital nature, it is easy to share, copy and reproduce. Buyers of NFTs need to understand that they would be infringing the copyright if they engage in such activities without the permission of the right holder. The only way such rights can be transferred is through the terms embedded in the NFT, in the form of a licence.
There have been some NFTs where the buyer has been granted the right to use the copyright in a limited way. For example, owners of CryptoKitties NFTs have been allowed to make up to US$100,000 in gross revenues from them each year. In other cases, creators have specifically restricted all commercial use of the work. For example, the Kings of Leon stipulated that their NFT music was for personal consumption only.
Buyers therefore need to be clear that the main reasons to buy an NFT are the speculative investment and the pleasure of having something unique from an admired artist, brand, sports team, or whatever. Unless the terms allow it, buyers will only have a limited ability to share the creative work on public platforms or to reproduce it and make it available for others.
Incidentally, buyers should also be aware that the blockchain cannot absolutely know whether a creative work is authentic. Someone can take another person’s work and tokenise it as an NFT, thereby infringing the rights of the copyright owner. You need to be sure that you are buying something that originated from the creator.
In short, NFTs are probably here to stay, but they clearly raise ownership questions relating to copyright law. This may not be immediately clear to most people, and it’s important that you understand the limits of what you are getting for your money.
Dinusha Mendis, Professor of Intellectual Property and Innovation Law and Acting Deputy Dean (Research), Faculty of Media and Communication, Bournemouth University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.












